ABSTRACT
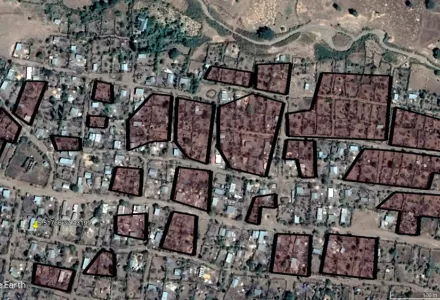
Earth observing remote sensing technology offers a pioneering method for gathering data on collective violence that would otherwise remain unseen, unreported, and unrecorded. However, it remains a critically underutilized tool in the academic study of conflict. This article demonstrates the value added of remote sensing by outlining a method that relies on publicly available satellite data of fires in conjunction with other satellite imagery to gain insight into bouts of intercommunal violence, which are subject to reporting bias. I use anomalous fire patterns as leads to identify potential conflict events and satellite images to determine the conflict relevance of fire detections by analyzing structural damage and scorch marks. I illustrate the contribution of this method by applying it to two cases of intercommunal violence: one in Cameroon's Far North Region and the other in Ethiopia's Southern Nations, Nationalities, and Peoples Region. I find 28 destroyed settlements in the former case, and 14 in the latter, most of which were previously unreported. Finally, the method has important academic and humanitarian use cases as a low-cost way of gaining near real-time and spatiotemporally accurate insight into the extent and spread of violence in conflict vulnerable areas.